Qt Creator
Qt Creator is a cross-platform C++, JavaScript, Python and QML IDE.
This article will show you how to configure and develop KDE projects in Qt Creator with kde-builder. We will use KCalc as an example project.
Install Qt Creator
sudo apt install qtcreator | |
sudo pacman -S qtcreator |
If you want to use a more recent version of Qt Creator than your distribution provides, you can install Qt Creator as a component in the "Qt online installer". See Use Qt6 from the online installer for details.
You may also build Qt Creator from Git.
KDE Builder configuration
To allow kde-builder to generate Qt Creator project files, set the following to your ~/.config/kde-builder.yaml:
generate-qtcreator-project-config: trueInstead of enabling the generate-qtcreator-project-config option globally, you may choose to enable it only for a single project:
override kcalc:
generate-qtcreator-project-config: trueEnsure you have successfully built kcalc following the kde-builder instructions.
In case you enabled generate-qtcreator-project-config after you have already built kcalc, or in case you do not want to edit your config, you can generate QtCreator
configs by running:
kde-builder kcalc --no-include-dependencies --no-src --build-system-only --generate-qtcreator-project-configApplying project configuration in Qt Creator
Unfortunately, Qt Creator has limited abilities for generating project configuration externally (for more info, see the kde-builder developer documentation). So the configuration is made half manually and half automatically.
See the official Qt documentation on Configuring Projects.
Opening project
From the Qt Creator main menu, select File | Open File or Project or press Ctrl + Shift + O and select the ~/kde/src/kcalc/CMakeLists.txt file.
Note
In case you want to start configuration from scratch, just delete the generatedCMakeLists.txt.user file and reopen a project.See the official Qt documentation on Opening projects.
Selecting Kit
If you are opening the project for the first time, the "Configure Project" view will be opened.
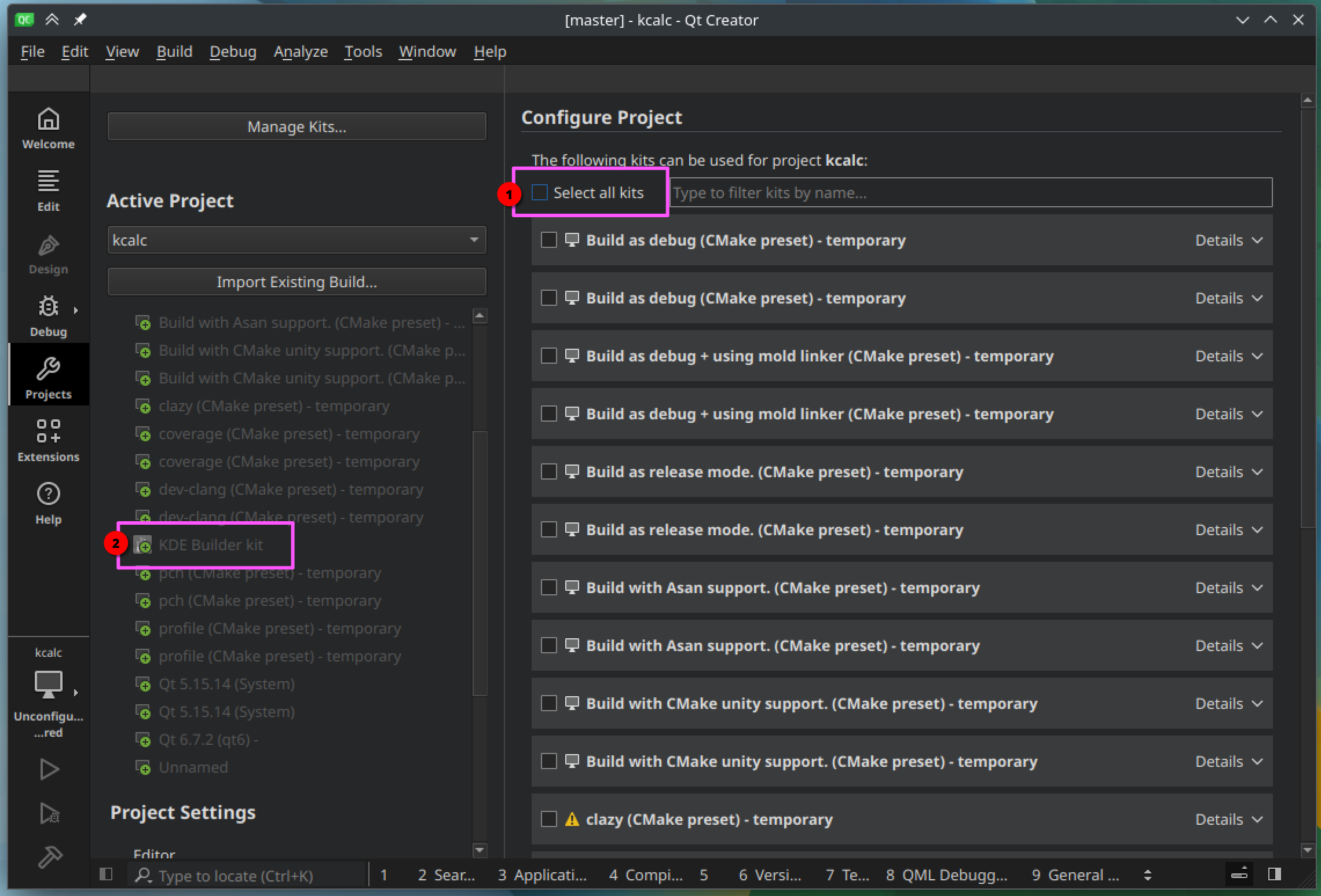
Press the "Select all kits" checkbox several times to deselect every kit. Then create "KDE Builder kit" (if not done yet), and select it.
Temporary kits
If the project has a CMakePresets.json in its root directory (KCalc does), you will see many temporary kits created for the project. You do not need them,
and need to deselect all of them.
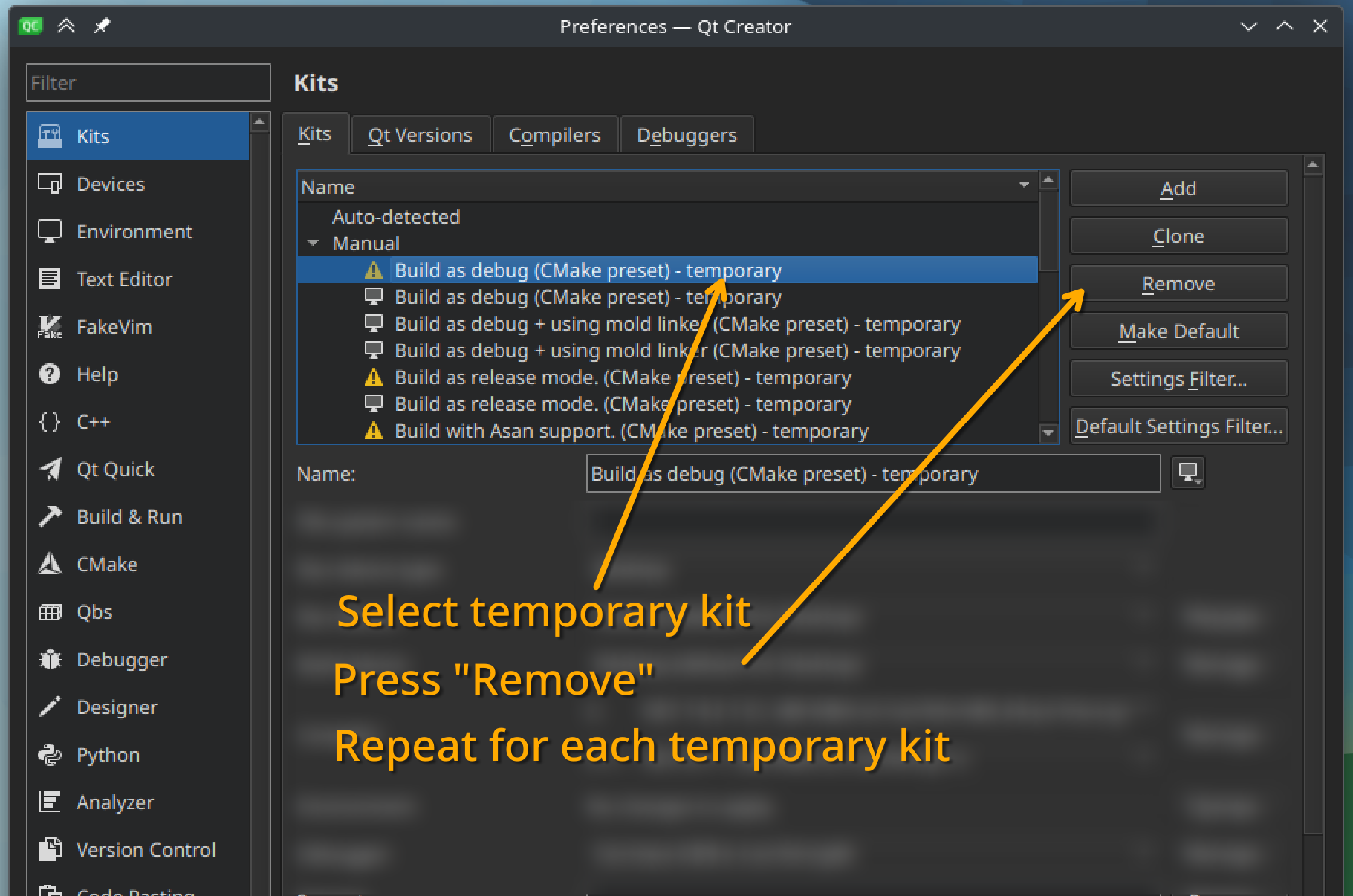
For your convenience, you can remove all temporary kits from the project, so they are not shown in the available kits in the Project mode. You can do this in "Manage Kits". In case you want them in the future, you could do Build | Reload CMake Presets.
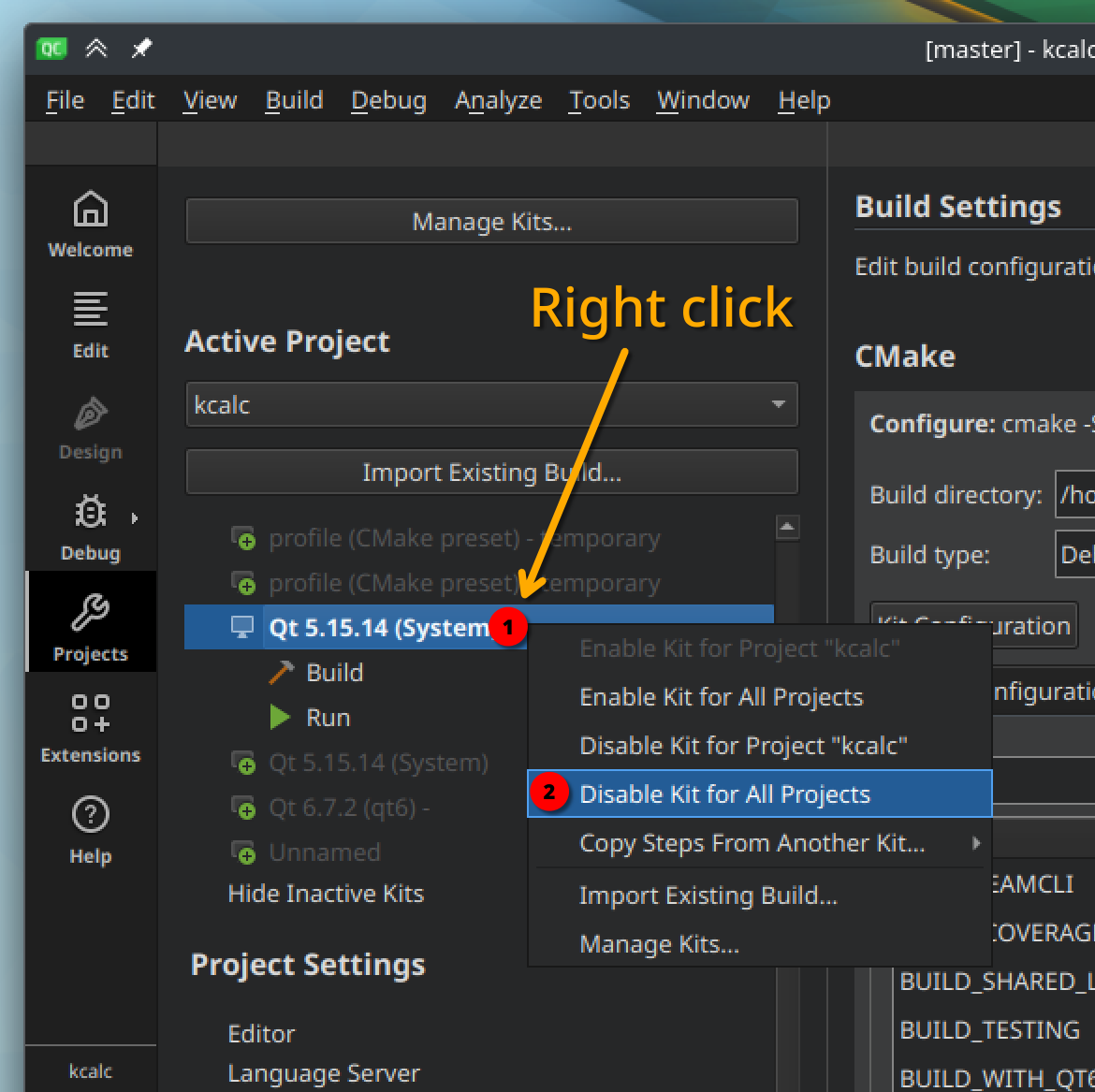
Alternatively, you can keep temporary kits there, but deactivate them for the project. If you accidentally clicked on an unwanted kit in "Build & Run", it got activated. To disable it again, click on its name with right mouse button, and select "Disable Kit for all projects".
Creating the KDE Builder kit
The very first time you want to use kde-builder with Qt Creator, you will need to create a kit named "KDE Builder kit".
Tip
This kit is a global IDE setting, so you will only need to do it once.In the left sidebar, switch to "Projects" mode (Ctrl+5), then click "Manage Kits...".
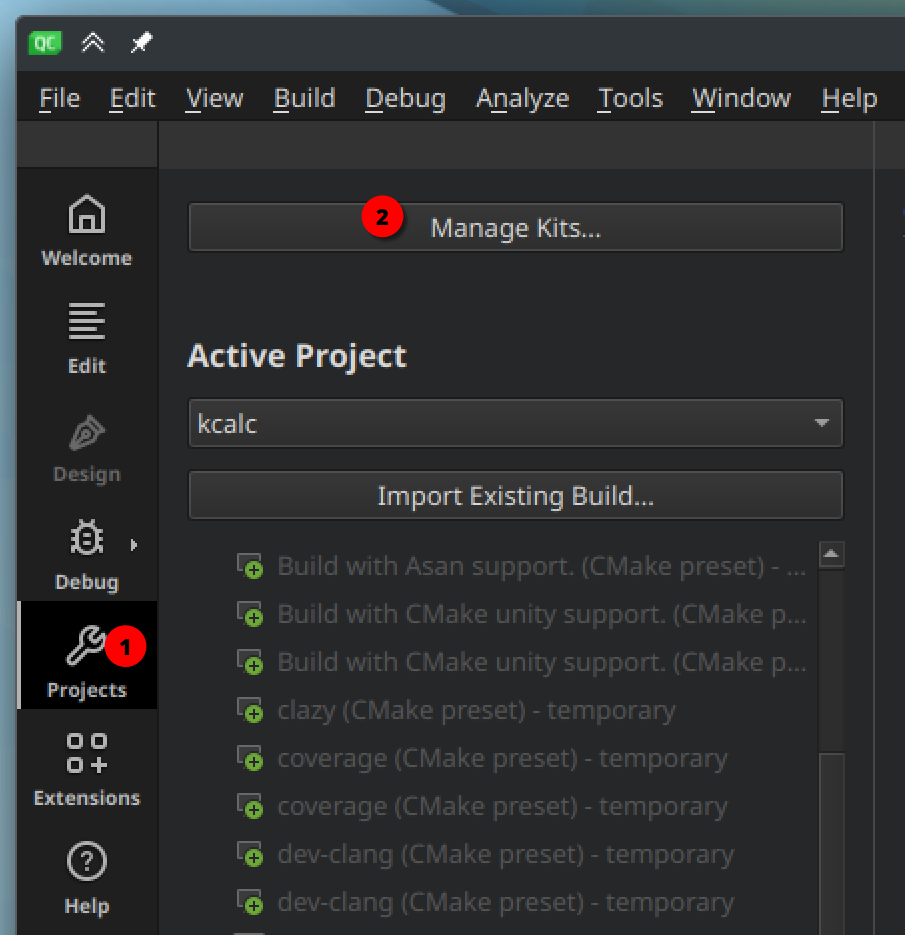
Press the "Add" button, and fill in the fields as follows:
Name: "KDE Builder kit"
Logo: select `~/.local/share/kde-builder/logo.png` (optional)
File system name: empty
Run device: Desktop (default for Desktop)
Build device: Desktop (default for Desktop)
Compiler:
C: select your GCC C compiler
C++: select your GCC C++ compiler
Environment: No changes to apply.
Debugger: /usr/bin/gdb
Sysroot: empty
Qt Version: None
Qt mkspec: empty
Additional Qbs Profile Settings: empty
CMake tool: /usr/bin/cmake
CMake generator: Ninja
CMake Configuration: (without them, our kit will have a warning that they are missing)
```
-DCMAKE_C_COMPILER:FILEPATH=%{Compiler:Executable:C}
-DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER:FILEPATH=%{Compiler:Executable:Cxx}
```
Python: None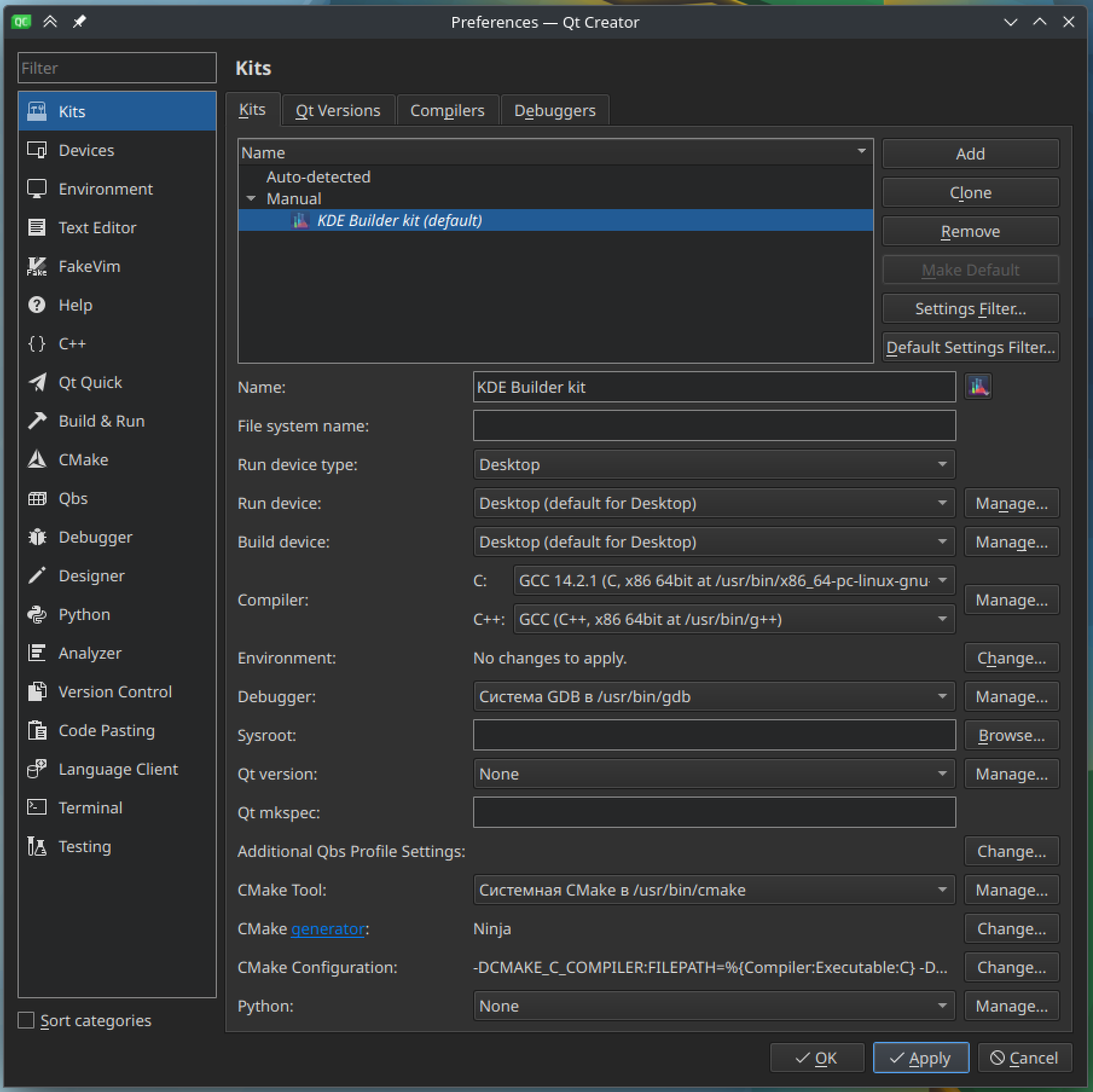
Configure Build Settings
Open the "Projects" mode (Ctrl + 5), go to "Build & Run", "KDE Builder kit", then click "Build".
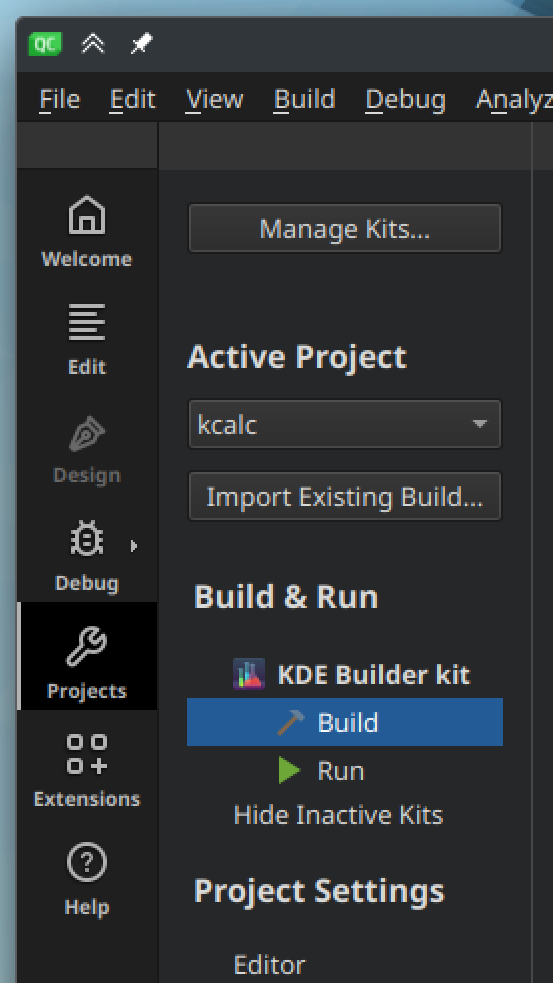
The "Build Settings" view will open.
Add new build configuration
Under the "Edit build configuration", press the "Add" button to add a new build configuration, select any type, for example, "Debug", and give it a name, for example, "KDE Builder build configuration".
CMake section
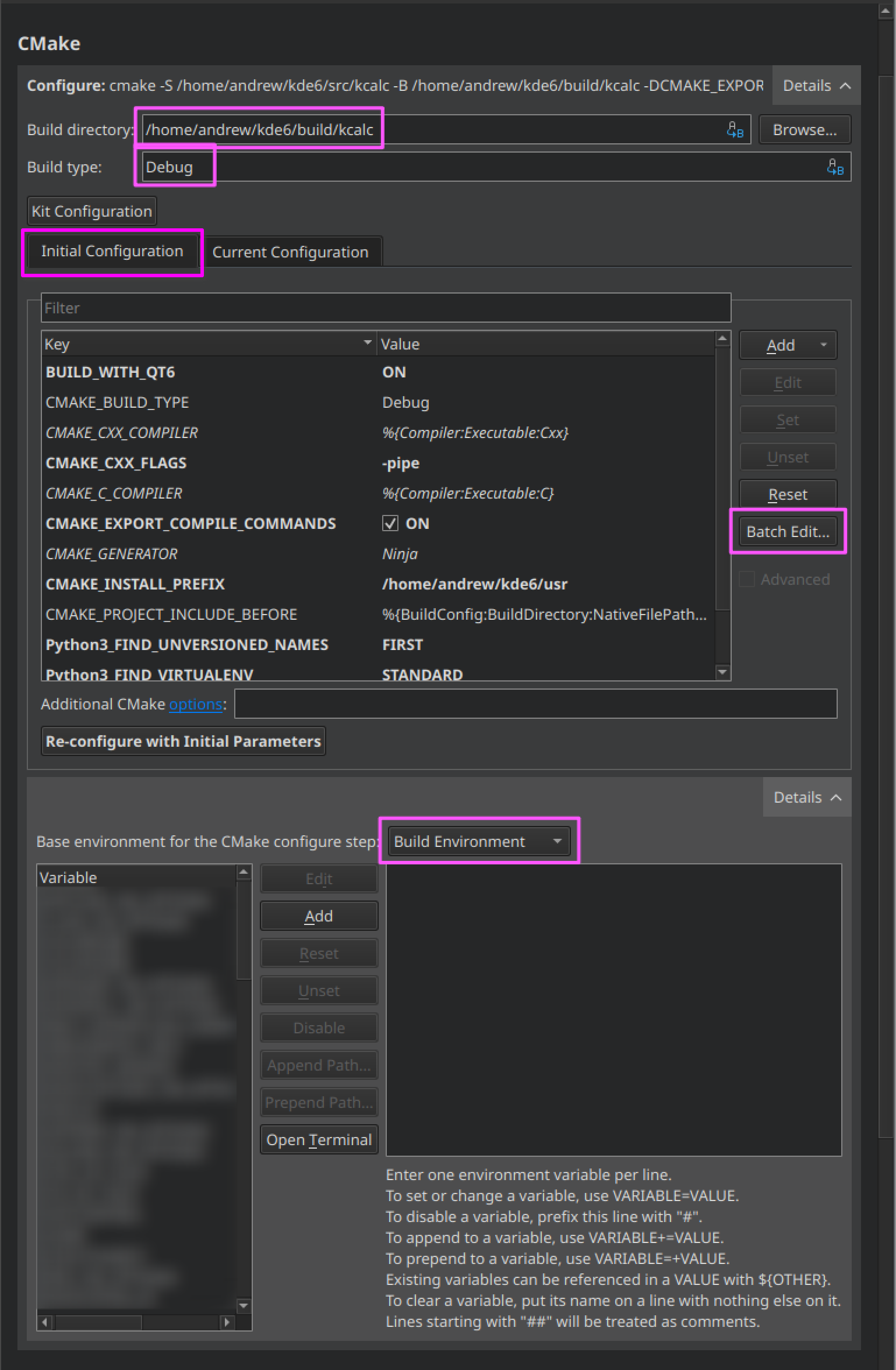
Under the "Build directory" field, enter the build directory of the module, in our example it will be ~/kde/build/kcalc.
Under "Build type", write the build type that was configured in kde-builder. This should be a valid value.
In the "Initial Configuration" tab, press "Batch Edit", then paste the text from the generated file located at
~/kde/src/kcalc/.qtcreator/cmake_Initial_Configuration.txt.
Under "Use Build Environment", press "Details" to expand this setting. Under "Base environment for the CMake configure step", select "Build Environment".
Build Steps section
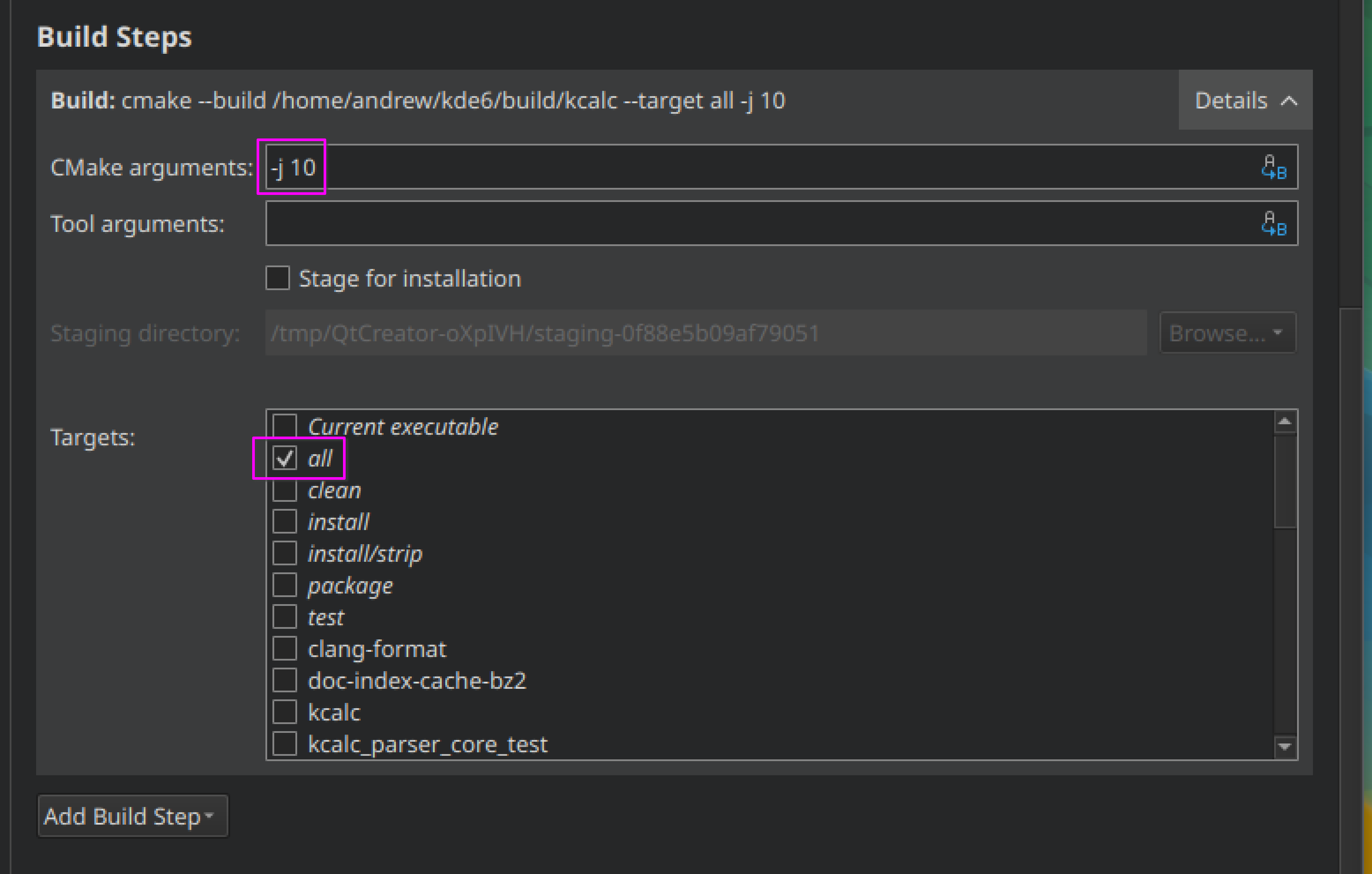
In the "CMake arguments" field, enter the "-j" and a value of your num-cores option, for example, "-j 10".
Under targets, ensure you selected "all".
Build Environment section
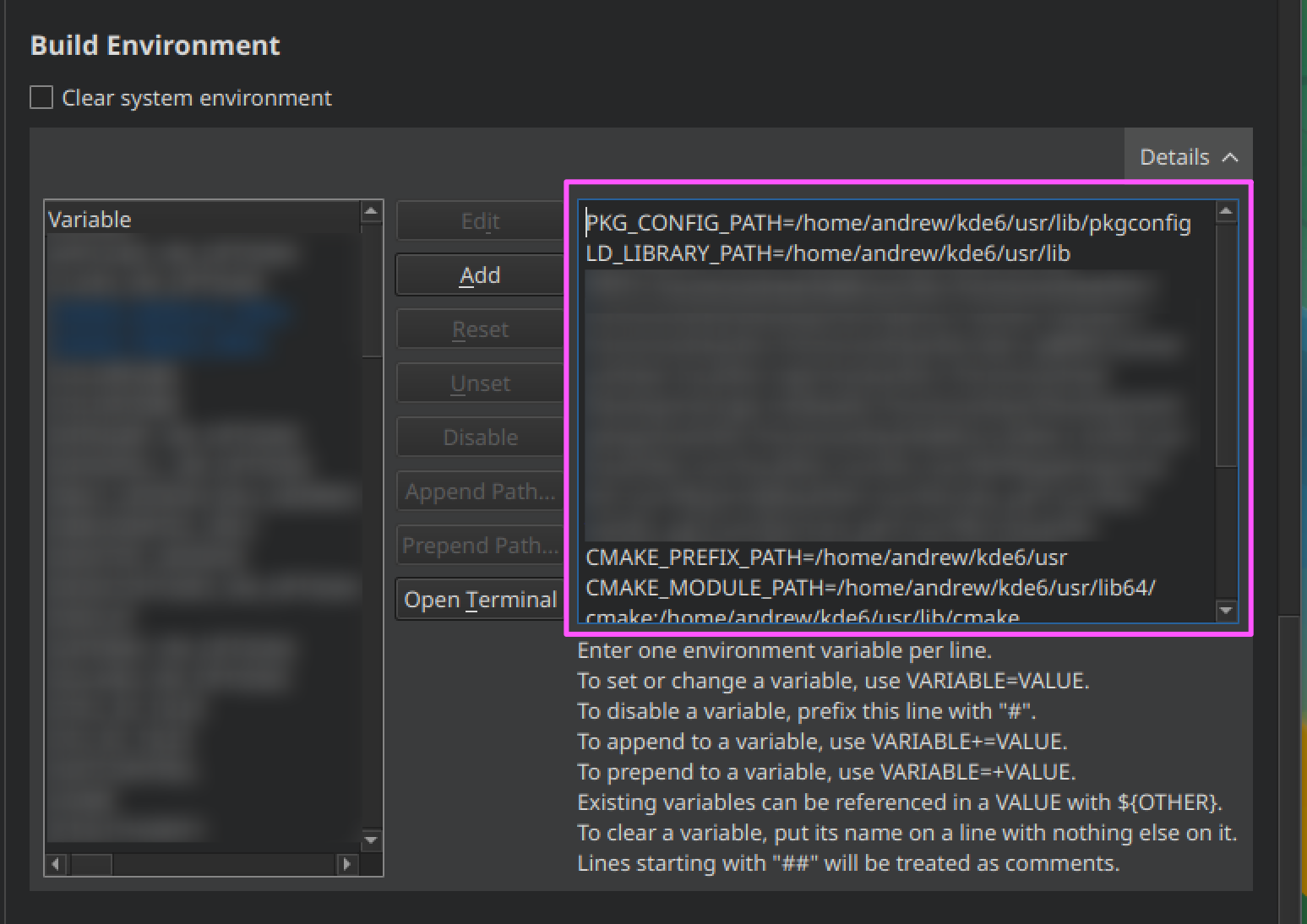
Copy the text from the generated file located at ~/kde/src/kcalc/.qtcreator/cmake_Configure_and_Build_Environment.txt and paste to the text field in this
section.
Configure Run settings
Open the "Projects" mode (Ctrl + 5), go to "Build & Run", "KDE Builder kit", then click "Run".
Deployment section
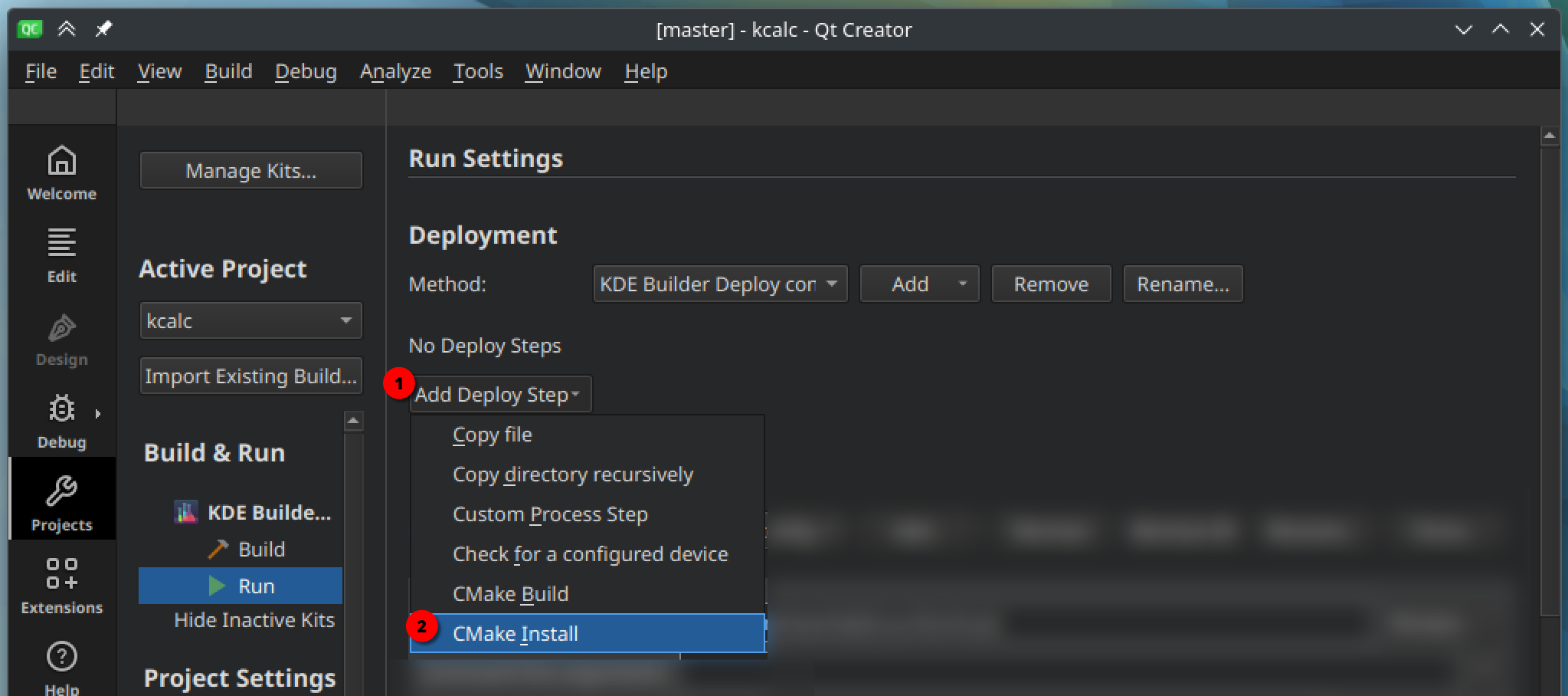
Under "Deploy configuration", press "Add Deploy Step" and select "CMake install".
For convenience, you can rename the configuration as "KDE Builder Deploy configuration"
Run section
In the "Run configuration" field, press Add button, and select "Custom Executable".
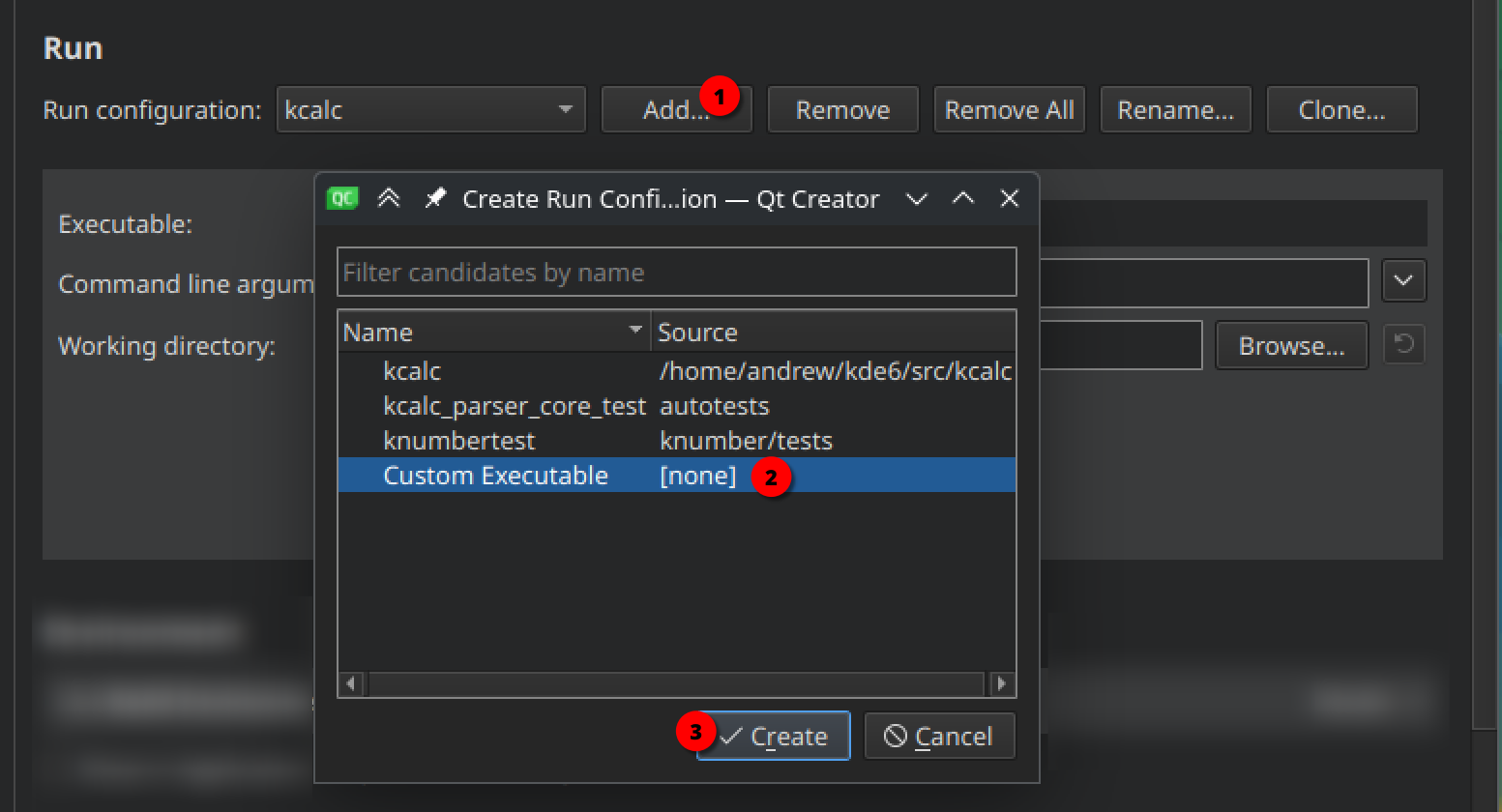
Rename the configuration for your convenience, for example as "KDE Builder Run configuration".
In the "Executable" field, specify the path to the installed project binary. In our example, it is ~/kde/usr/bin/kcalc.
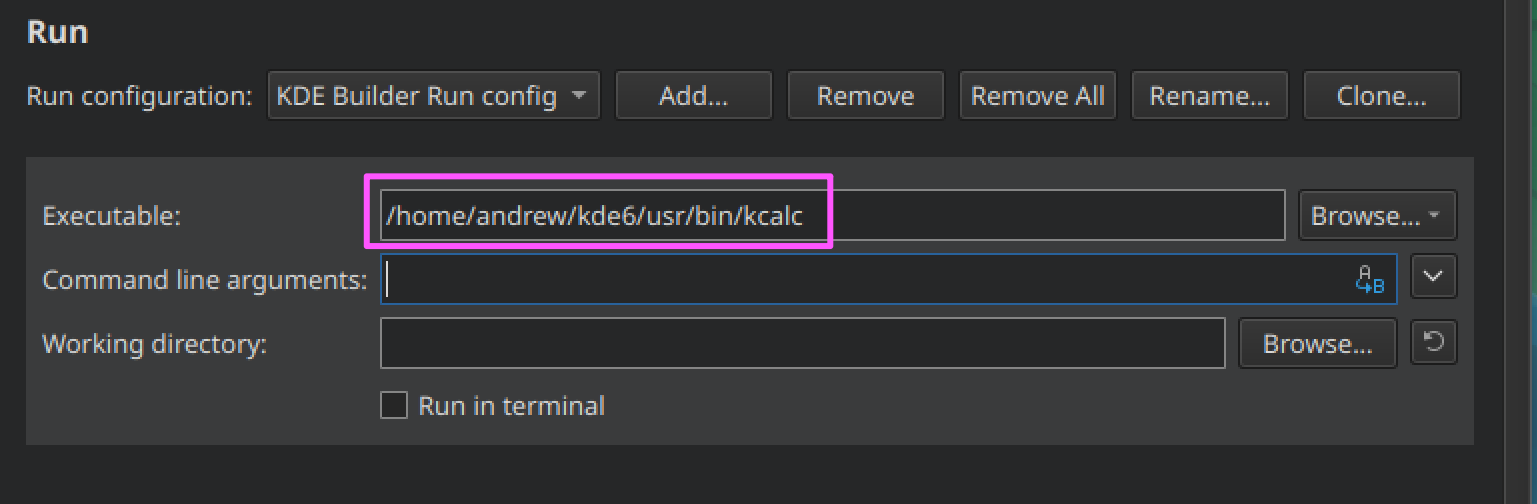
Environment section
Click "Details" to expand this setting.
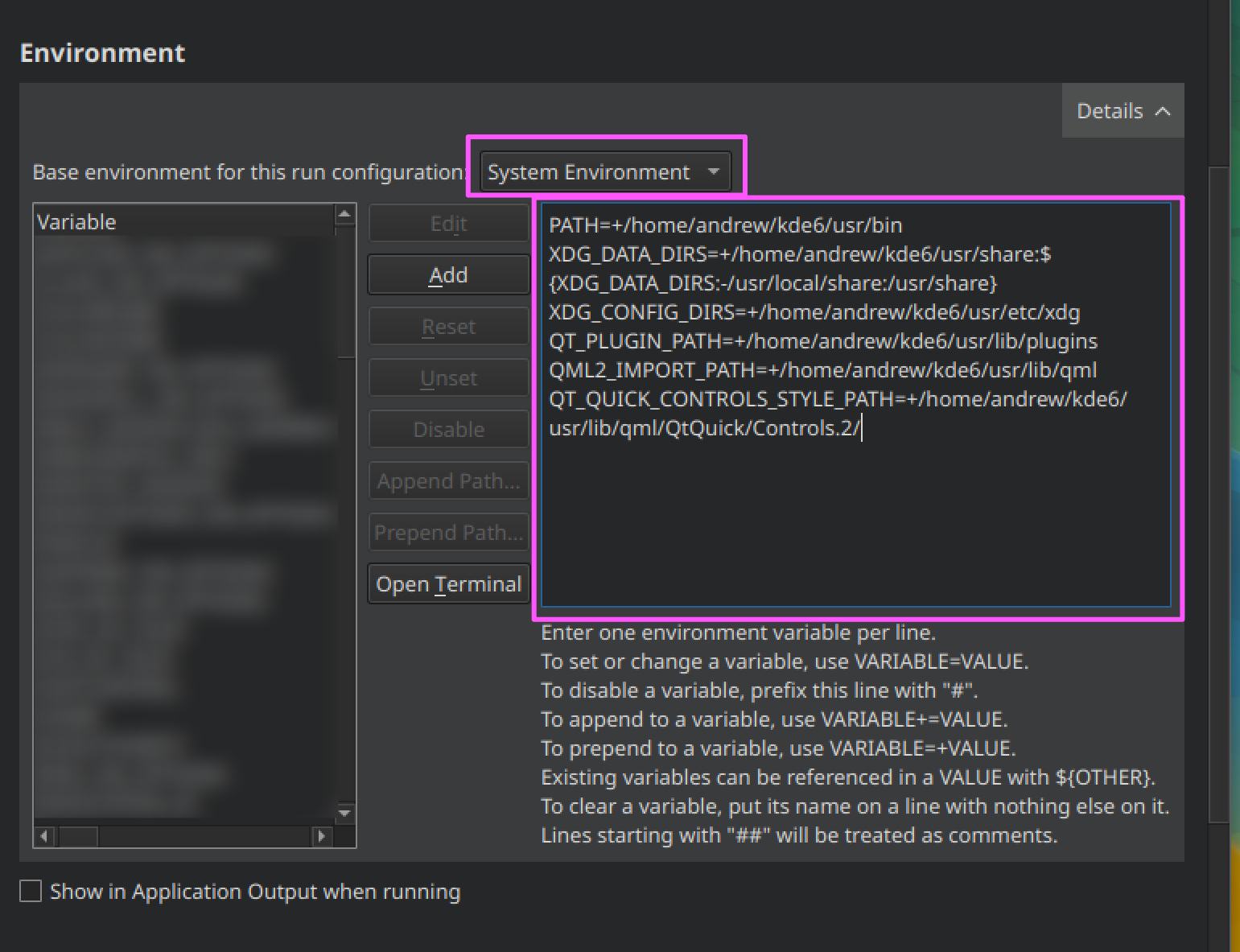
In the "Base environment for this run configuration" select "System Environment".
Copy the text from the generated file located at ~/kde/src/kcalc/.qtcreator/Run_Environment.txt and paste it into the text field in this
section.
Note: if you want to see debugging messages, you can add corresponding variables here. See Using error messages for more information.
Start developing
In the left bottom corner, in the configuration selector, ensure the correct configuration is selected (i.e. for the "kcalc" project, the Build, Deploy and Run configurations applied are those that we configured).
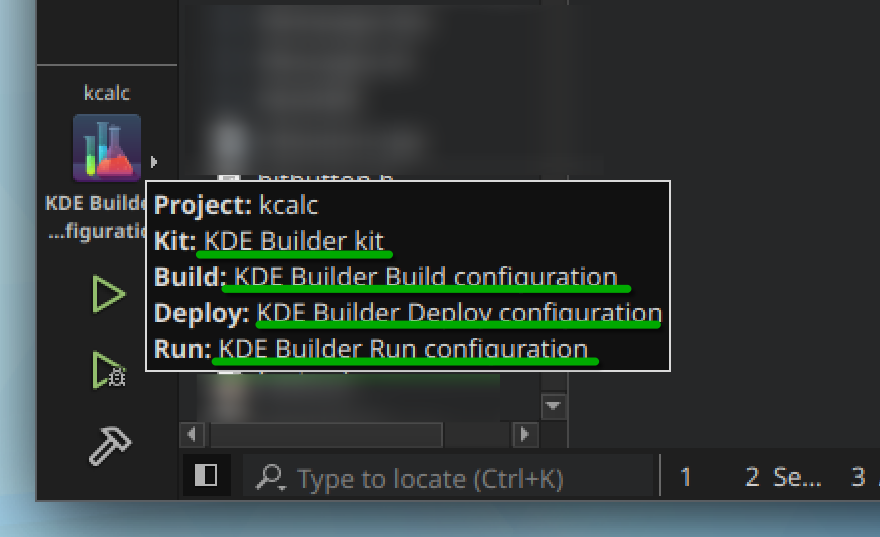
You are now ready to start developing.
Switch to "Edit" mode (Ctrl + 2). Open the kcalc.cpp, and make a breakpoint. For example, let's do it in main(). In the text editor's top bar, open the "Select Symbol"
drop-down menu, scroll to the bottom of the options, and select the last item in it: main(int, char**) -> int. Click on the line with the opening curly bracket of the
function main().
Now when you click the Debug button (that has a green play icon with a bug in its corner), all the preparation steps will be done automatically (CMake configure, build, deploy and run).
The debugger will stop at the breakpoint, and you can inspect variables, step into functions, etc.
Tips and Tricks
Custom executable to run
When developing a library, it may be convenient to launch some application that uses it, from the current project. For example, you work with Ark's
libraries used in Dolphin's context menu actions. You can make your run configuration to launch the custom binary dolphin.
See Qt Creator settings: Specifying a custom executable to run to configure that.